 |
|
|
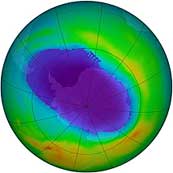
Our planet has a natural defence against the Ultraviolet radiation that is coming from the Sun. High in the atmosphere there is a layer of Ozone gas – O3 – made up of molecules of three oxygen atoms together. As the photons of UV strike a molecule of ozone, it absorbs it, breaking it down into oxygen again. This stops the UV from getting through to the surface of the earth. Over recent decades there has been a problem with this protective layer. Gases called CFCs, that are produced as part of modern life, destroy the ozone. (These are primarily used in refrigeration). As the ozone layer decreases, the amount of UV that gets through increases, making sunlight even more dangerous. More recently there have been international efforts such as the Montreal Protocol to reduce the volume of CFC gases that are released into the atmosphere. As a result the size of the hole in the ozone layer seems to be reducing.
|


 More info
More info More info
More info Sunscreen
Sunscreen
What's your opinion?
Average rating




Not yet rated